
川西 昌浩
- 副院長

ヘルスケアソリューションの情報発信誌「Future of Healthcare Vol.11」に当院の血管撮影装置「ARTIS icono D-spin」について掲載されました。

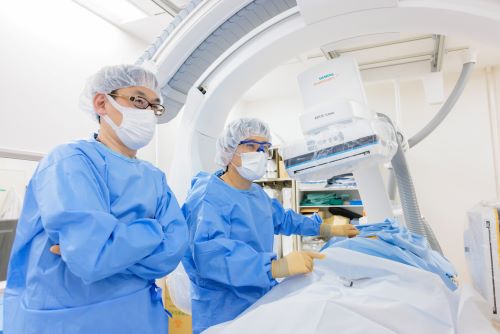
当科では、この20年間にわたり、従来からの開頭外科的手術、脊椎・脊髄と末梢神経の手術、そしてカテーテルを使った血管内治療を3本の柱として、疾患と患者さんの状況にあった適切な治療の提供につとめています。
具体的な例で順に説明しますと、開頭や首の切開など、直接目で見て顕微鏡を使って治療するのは最も得意とするところですが、何でもかんでも切るのではありません。
従来の開頭手術のように頭部にメスを入れることなく、主に大腿動脈からカテーテルを脳内や顔面の末梢血管まで挿入して行う血管内手術を積極的に行なっており、非常に困難な症例に関しても良好な結果が得られています。特に、施設・術者限定にしか供給されない一部の頭蓋内ステントや液体塞栓物質などを用いての治療も対応しております。血管内治療で治療可能な疾患は第一選択としています。なお、血管内手術で治療できる主な疾患には以下のものがあります。
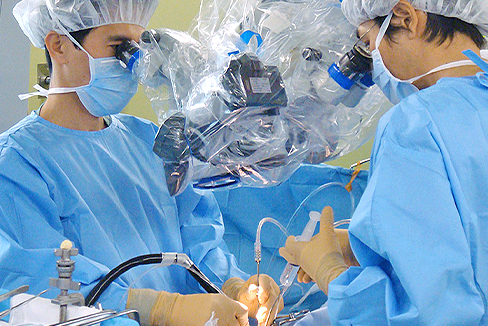
脊椎の治療も同様です。従来は大きく切開して、患部がよく見える状況にして切除して、固定するというのが一般的な治療でしたが、現在ではできるだけ切開する範囲を狭くし、可能な限り患者さんへのダメージを減らして修復していくことを治療の方針としています。
背骨は体にとって動く柱ですから、削る範囲をできるだけ小さくしてグラグラしないようにします。このことによってネジで固定することを減らすことができるわけです。どうしてもネジを入れる必要がある場合でも、できるだけ筋肉を切らずに治療を行います。背中の筋肉は腰痛に関連しており、これを切ると、回復する期間が長くなるからです。当院では脊椎手術後は、翌日より起立歩行可能で、抜糸後退院となります。高齢者に多い圧迫骨折の場合は骨に医療用のセメントを注入する「経皮的椎体形成術」を行うことで、できるだけ早く痛みをとって早く家庭復帰できるようにしており、当日ないし翌日退院が可能です。
このように、いずれの治療法についても、患者さんの負担ができるだけ少なくし、スムーズな社会・家庭復帰が出来るよう「低侵襲」な医療となることを目指しています。
当科は、さまざまな脳・脊髄神経疾患の症状に応じた検査・治療を実施しています。
頭痛、めまい、物忘れなどはもとより 顔手足の痛み、手足のしびれ、筋力低下、歩行障害、腰痛、背部痛、下肢痛などの症状につき治療を行っています。これらの訴えに応じた最も適切な検査を選択し、インフォームドコンセント・セカンドオピニオンを重視し、患者さん・ご家族の同意のもとに、治療方針を決定しています。
脳卒中に対しては専門の脳卒中ケアユニットを併設し、救急隊の要請はもとより、近隣の開業の先生方との“病診連携”により、くも膜下出血、脳出血、脳梗塞、頭部脊椎外傷など緊急を要する依頼に対し、SCUホットラインを設けて、24時間、365日、脳外科医が対応可能な体制を採っています。

当施設は日本脳神経外科学会専門研修プログラム連携施設(基幹施設番号53 施設番号276号)及び日本脳脊髄外科学会認定訓練施設(21号)です。また、急性期脳梗塞に対するt-PA,血栓粉砕治療実施の認可施設です。圧迫骨折に対する風船治療の認可施設です。
診断機器はCT、3DCT、MRI、超音波、脳血管撮影装置、パーフュージョンCT血流動態検査、電気生理学的検査(SEP、ABR、NCV)などを完備しています。脳神経専門の検査技師、放射線科技師と密接に症例検討を行っております。
脳血管撮影装置は最高機種のバイプレーンフラットパネルを導入しており、超微細な脳血管内治療が可能となっています。また、手術室には回転Cアームとナビゲーションシステムをもち、手術を低侵襲、安全に実施可能となっています。脊椎疾患や末梢神経疾患は当院神経筋外来の協力のもと電気生理学的検査(SEP、NCV)などによる客観的評価を必須とし、また脳血管障害はすべて専門技師により超音波を用いた全身の脈管学的精査フォローを行っています。
主な治療対象疾患は、脳腫瘍、脊髄腫瘍、くも膜下出血、未破裂脳動脈瘤、脳動静脈奇形、脳内出血、脳梗塞等の脳血管障害、急性硬膜外・下血腫、脳挫傷、慢性硬膜下血腫等の頭部外傷、脊髄損傷、頸椎症、頸椎椎間板ヘルニア、腰部脊柱管狭窄症、腰椎すべり症、圧迫骨折、腰椎椎間板ヘルニアなどの脊椎疾患、手根管症候群、肘部管症候群などの末梢神経疾患、顔面けいれん、三叉神経痛などの機能的疾患など脳神経外科全般にわたります。
また、従来の開頭手術のように頭部にメスを入れることなく、大腿動脈からカテーテルを脳内の血管や顔面の血管まで挿入して行う新しい治療手段“血管内手術”により、非常に困難な症例に関しても良好な結果が得られています。血管内治療で治療可能な疾患は第一選択としています。尚、血管内手術で治療できる主な疾患には以下のものがあります。
脊椎圧迫骨折に対しては、経皮的椎体形成術(セメント治療)を平成15年7月から実施し600症例を超えました。除痛効果に優れ、日帰り治療が可能です。

平成23年からは、風船を用いたセメント治療(バルーンカイフォプラスティ:BKP)を開始しております。
こちらに関しては、健康保険の適応です。
※動画提供元の「先進医療推進機構(AMPO)」がサイト閉鎖のため、当院のYouTubeからご覧ください。

外科診療にとりもっとも大きなウェートを占めるのは手術成績であり、成績・手技向上のため、手術全過程をビデオに記録保存、デジタル化することにより、論文、学会、他施設との症例検討会などを通じて公表、他者評価を受けるようにしています。また、後輩やパラメディカルの指導に用いています。手術症例は全てデータベース化し、検索、集計、発表ができるようにしています。
論文発表・学会活動を通じて他者批判を乞うとともに、最先端の治療行為は他大学や外国での遺体解剖による手術訓練を行い、研究所での動物実験にて修練を積んでいます。また後進の教育方針としては、開頭手術、脊椎・末梢神経手術、血管内手術を3本の柱としていずれにも対応できる脳神経外科専門医を養成しております。手術室以外での顕微鏡手術修練(off job)を行っています。具体的には以下のプログラムを実施しています。
当診療科では、下記事業に参加しています。詳しくは、以下をクリックして下さい。
脳卒中は、脳の血管が詰まる脳梗塞、高血圧などにより血管が切れる脳出血、特に脳動脈瘤が破裂するクモ膜下出血、に分類されます。降圧・脂質管理を主とした予防医療の進歩により脳出血は減少しました。しかしクモ膜下出血は減少しておらず、脳梗塞はむしろ増加している現状です。
脳卒中は、がん・心臓病に次いで死因第3位であり、年間13万人くらいの方が亡くなっています。寝たきりになる原因の3割近くを占め、第1位です。高齢化社会や生活習慣病の増加もあり、毎年25万人以上が新たに発症されています。全国の患者数は2020年には250万人、約60%が要介護と試算されています。
このような社会背景に適した脳卒中の対応が望まれます。つまり、脳卒中に対して予防治療から急性期・亜急性期・慢性期治療、在宅医療まで統合的・系統的な対応が必要と考えられます。これには、医師、看護師、リハビリテーション療法士などの医療従事者および医療ソーシャルワーカーによるチーム医療、近隣のリハビリ病院、掛かり付け医、介護施設などとの連携の整備が不可欠です。
脳卒中ケアユニット(stroke care unit:SCU)とは、脳卒中急性期の患者さんを専門医療スタッフが、急性期の集中治療とリハビリテーションとを組織的、計画的に行う脳卒中専用の治療病棟のことです。脳卒中治療ガイドライン(2009)では、SCUで治療することによって、脳卒中患者の死亡率の低下、在院期間の短縮、自宅退院率の増加、長期的な日常生活動作(ADL)と生活の質(QOL)の改善を図ることができるという検証結果が示されました(グレードA)。
当科ではこのような社会・地域の要望にこたえるために、厚生労働大臣の定める施設基準を満たすSCUを6床開設、脳卒中センターを設立し、脳卒中急性期の受入れ・治療を今まで以上に充実させて頂きました。脳卒中専門医を含む脳神経外科または神経内科の経験あるスタッフが24時間対応致します。脳卒中の可能性の高い症状を示す患者さんはできる限り早くご連絡下さい。脳卒中かどうかの判断が困難な患者さんも遠慮、躊躇なくご相談下さい。
尚、SCUおよび脳神経外科の病床数は限られております。治療・診療経過に応じて、更なるリハビリが必要な患者さんには地域連携パスによる回復期リハビリ病院への転院、その他の介護施設・療養型病院などへの転院マネージメントも行わせて頂いております。
当院で行われている診療は、論文、ビデオ発表、学会などを通じて、英文、和文問わずに広く公表しております。
患者さんの負担の少ない医療の推進:当科で積極的に進めている脳血管内治療はもちろんのこと、従来の外科治療を常に再検討し、最先端の医療を柔軟に選択していくことが必要と考えています。脊椎圧迫骨折に対する経皮的椎体形成術(セメント治療)を平成15年7月から導入し600症例を超えました。
セメント治療は当施設が学会事務局となり、安全な治療となるべく、学会を主宰しています(※)。なお圧迫骨折に対するセメント治療は、最新医学新書(最新医学社)「腰痛治療の最前線―圧迫骨折はセメントで直せー」にて紹介しております。
また脊椎手術は従来のように大きくきるのではなく、顕微鏡やナビゲーションを駆使して、小さな傷で行い、痛みを極力減らす努力をしています。手術翌日には全例歩行が可能です。
※椎体形成術研究会(事務局:医仁会武田総合病院 脳神経外科 川西昌浩)
山下 正真
ご連絡・アクセス方法